Everything You Need to Know About Google Search Console
admin
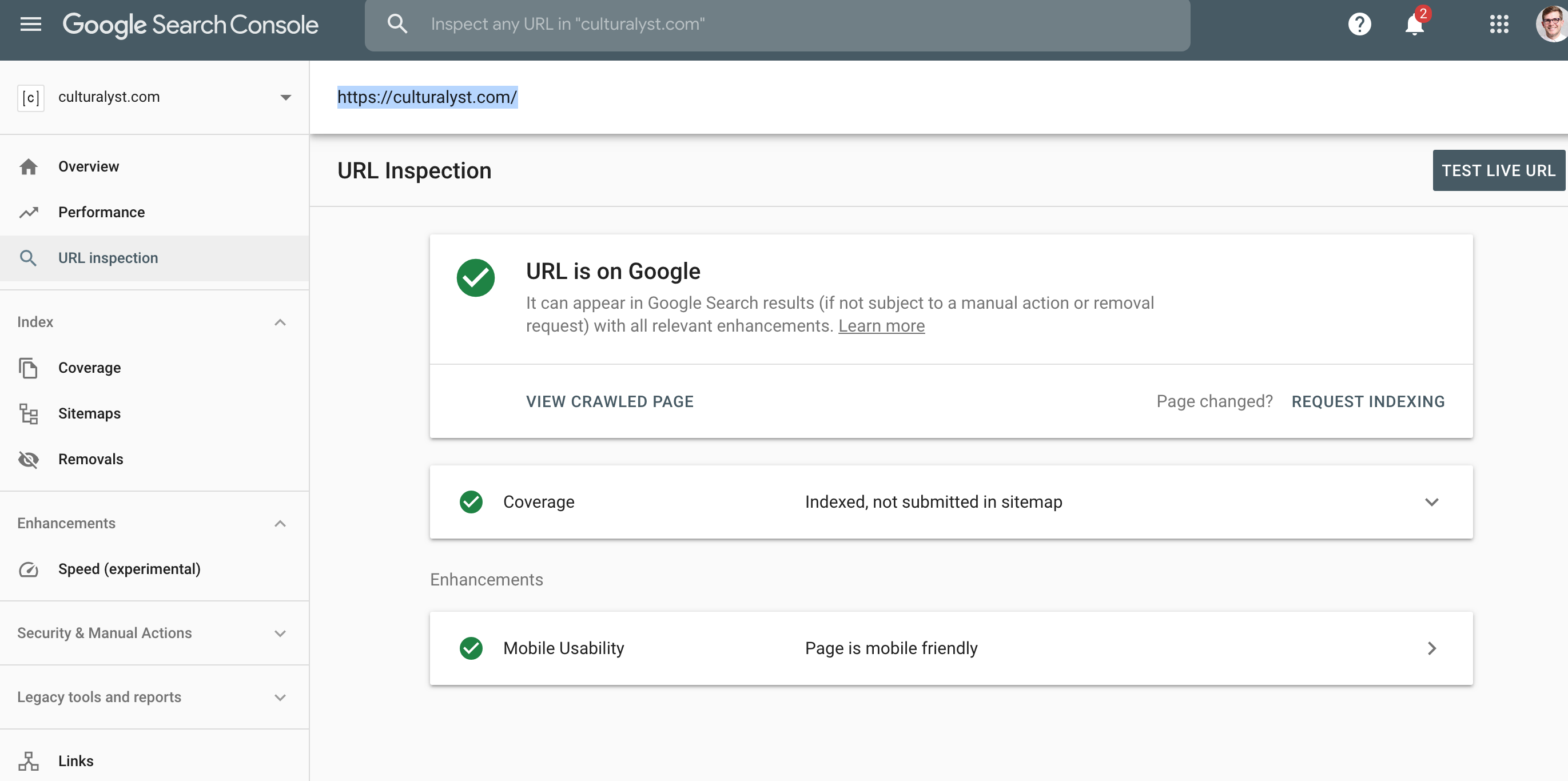
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Google Webmaster, now Google Search Console, is a vital tool for tracking and optimizing your website’s performance in search results. This guide will help you understand how to add your site, navigate the menus and reports, and submit a sitemap for better indexing.
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console, is a free tool by Google that helps website owners monitor, optimize, and improve their site’s visibility in search results by providing insights on performance, indexing, and potential issues.
To access it, visit search.google.com/search-console and sign in with your Google account.
How to Add Website in Google Search Console?
To add a website to Google Search Console (Google Webmaster), follow these steps:
- Sign In: Go to Google Search Console and log in with your Google account.
- Add Property: Click the “Add Property” button on the dashboard.
- Enter Website URL: Choose between two options:
- Domain Property: Covers all URLs across subdomains and protocols (e.g., http, https). Enter your domain name, like example.com.
- URL Prefix Property: Covers only URLs with the specified protocol (e.g., https://example.com).
- Verify Ownership: Prove that you own the website by completing one of these verification methods:
- DNS Verification: Add a TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings.
- HTML File Upload: Upload a specific file to your website’s root directory.
- HTML Meta Tag: Add a meta tag to your site’s <head> section.
- Google Analytics or Google Tag Manager: Use an existing Google account associated with your website.
- Confirm Verification: After completing the selected method, click the “Verify” button.
- Start Managing Your Website: Once verified, you can begin using Google Search Console to monitor and improve your website’s performance.
What URL prefix should I add if the website is already indexed?
If your website is already indexed, go to Google.com and search for the indexed version. Use the site operator to find which URL prefix is indexed by Google, e.g., site:example.com. Add the indexed URL prefix in Google Search Console.
What should I do if website clicks drop in Google Search Console after installing SSL?
If your website’s clicks drop after installing SSL (switching from HTTP to HTTPS), add the HTTPS version to your Google Search Console by clicking the ‘Add Property’ option. Also, check if the HTTP URL prefix is properly redirected to the HTTPS version.
Google Search Console Menus and Reports:
1. Overview
The Overview page gives a snapshot of your site’s overall performance. It includes key metrics like clicks, impressions, average position, and click-through rate (CTR) in search results.
2. Performance
The Performance report displays detailed metrics on how your site is performing in Google Search:
Total Clicks: The total number of clicks your site received from Google Search.
Total Impressions: The total number of times your site appeared in search results.
Average CTR: The average click-through rate, showing the percentage of impressions that led to clicks.
Average Position: The average ranking position of your pages in search results.
You can filter by queries, pages, countries, devices, and dates.
3. URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool allows you to check how Googlebot views a specific URL. It shows:
Indexing status: Whether the page is indexed or not.
Crawl status: Information about the page’s last crawl and any errors.
Mobile usability: Details about how the page appears on mobile devices.
Rich results: Whether structured data is properly implemented for enhanced results.
4. Indexing
Indexing refers to the process by which Google organizes and stores web pages it has crawled, making them available in search results. It determines whether a page can appear in Google’s search rankings.
These tools under the Indexing tab help you understand and manage how your site’s pages are indexed
- Pages: The Pages report contains data about indexed and non-indexed pages. It provides information on:
- Valid: Pages that are successfully indexed.
- Error: Pages that could not be indexed (e.g., due to server issues or crawl errors).
- Valid with warnings: Pages that are indexed but may have issues (e.g., mobile usability problems).
- Excluded: Pages that were intentionally or unintentionally excluded from indexing.
Additionally, the report highlights reasons why pages aren’t indexed, such as:Pages with redirects.
- Pages blocked by robots.txt.
- Pages excluded by a noindex tag.
- Pages blocked due to other 4xx errors.
- Alternate pages with proper canonical tags.
- Pages crawled but currently not indexed.
- Pages discovered but not yet indexed.
Sitemaps: The Sitemaps section lets you submit XML sitemaps to Google, helping the search engine discover all the important pages on your site. It also shows whether Google has encountered any issues while crawling your sitemaps.
Removals: This section allows you to temporarily remove URLs from Google’s search results. You can also check requests related to outdated content or SafeSearch filtering.
5. Experience:
There are two key reports under the Experience tab in Google Search Console:
Core Web Vitals: This report provides insights into the user experience of your site, focusing on metrics like loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. It highlights issues that may affect the overall user experience on both mobile and desktop devices, such as slow page loads or content shifts, helping you optimize for better performance.
HTTPS: This report tracks the status of your site’s HTTPS implementation. It identifies any potential issues with HTTPS, ensuring that your website is securely accessible. A proper HTTPS setup is crucial for user trust and SEO rankings. This report helps you monitor and maintain secure connections across your site.
6. Enhancements
In the Enhancements section, you can find reports that help improve the user experience and site performance, such as:
Breadcrumbs: Displays issues related to the breadcrumb structured data on your site, helping search engines better understand the page hierarchy and improve navigation for users.
Product: Displays errors related to the structured data for product pages, helping enhance their visibility in search results.
FAQ: Reports issues with FAQ schema implementation, allowing for better presentation in Google’s search results.
Site Links Searchbox: Provides information on how your site links searchbox is implemented and any potential issues that could impact its functionality.
8. Links
The Links report provides insights into your website’s internal and external links:
Top linked pages: Displays the pages on your site that have the most external backlinks.
Top linking sites: Shows the external websites that link to your site the most.
Internal links: Lists the most internally linked pages on your website.
9. Manual Actions
The Manual Actions section shows if Google has taken any manual actions against your website due to violations of Google’s webmaster guidelines (e.g., unnatural backlinks or thin content). If your site has been penalized, this section will provide details and steps to resolve the issue.
10. Security Issues
The Security Issues report alerts you to any security problems detected on your website, such as hacking attempts, malware, or phishing. Google will notify you here if your site is compromised.
11. Settings
The Settings menu allows you to manage and configure your Google Search Console account, including:
1. Property settings: Edit your site’s URL and preferred domain settings.
2. Users and permissions: Add or remove users with different permission levels.
3. Associations: Connect your Google Search Console account with other Google services like Google Analytics.
4. Robots.txt: This report provides details about your robots.txt file, including its content, the date and time it was analyzed, and its size. It also indicates the file’s status, such as whether it is valid or has issues, and lists any errors or warnings detected during the analysis.
6. Crawl Stats Report: This report provides comprehensive data about how Googlebot crawls your website. It includes information such as the total number of crawl requests, the size of data downloaded, the server response time, and the breakdown of requests by response type (e.g., success, redirect, error). It also provides insights into how frequently Googlebot visits your site and identifies any crawling anomalies.
These menus and reports provide comprehensive insights into how your site is performing in search results, as well as guidance on how to improve its indexing, visibility, and user experience.
How do I add a sitemap in Google Webmaster?
To add a sitemap to Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster), follow these steps:
1. Prepare Your Sitemap
Make sure your sitemap is in XML format and contains a list of all important URLs on your website.
You can generate a sitemap using various tools or plugins (e.g., Yoast SEO for WordPress) or manually create it. Make sure your sitemap is in
XML format and contains a list of all important URLs on your website.
3. Navigate to the Sitemaps Section
On the left sidebar, scroll down and click on “Sitemaps” under the Index section.
4. Submit the Sitemap
In the “Add a new sitemap” section, enter the URL of your sitemap. For example:
If your sitemap is located at https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml, enter sitemap.xml in the field.
If you are using the Yoast plugin, your sitemap will be located at https://www.example.com/sitemap_index.xml. Enter sitemap_index.xml in the field.
Yoast categorizes your sitemap into different post types, and you can also add them to your sitemaps, e.g., Post-sitemap,xml, Page-sitemap.xml and Product-sitemap.xml etc..
5. Click “Submit”
After entering the correct URL, click the “Submit” button to submit your sitemap to Google.
6. Check for Status and Errors
After submitting, Google will process the sitemap and show its status in the “Sitemaps” section. It may take some time for Google to crawl and index your pages.
The status will show whether the sitemap was successfully processed or if there were any errors (e.g., invalid URLs, inaccessible pages). If errors occur, fix them and resubmit the sitemap.
How to request a web crawl in Google Search Console ?
To request a web crawl in Google Search Console, follow these steps:
- Sign in to Google Search Console: Go to Google Search Console and log in to your account.
- Select Your Property: If you have multiple properties, select the website you want to request a crawl for.
- Go to the URL Inspection Tool: In the left sidebar, click on “URL Inspection”.
- Enter the URL: In the search bar at the top, enter the specific URL of the page you want to be crawled. Press Enter.
- Request Indexing: Once the URL is loaded, you’ll see information about the page. If the page is eligible for indexing, you’ll see an option that says “Request Indexing”. Click on it.
- Confirm Request: Google will process the request, and after a short time, you should see a confirmation that the URL has been queued for crawling.
This process tells Google to crawl and re-index a specific page, helping it appear in search results more quickly if there have been recent changes.
How to delete a site from Google Search ?
To delete a site (property) from Google Search Console, follow these steps:
- Sign in to Google Search Console: Go to Google Search Console and log in.
- Select Your Property: If you have multiple properties, select the website you want to remove from the property list.
- Open Settings: In the left sidebar, scroll down and click on “Settings”.
- Manage Property Settings: Under the “Settings” menu, you will see a section called “Property Settings”.
- Remove Property: At the top right of the “Property Settings” page, you’ll find the option “Remove Property”. Click on it.
- Confirm Removal: A pop-up will appear asking you to confirm that you want to remove the property. Confirm your choice by clicking “Remove”.
Important Notes:
- Deleting a property in Google Search Console does not affect your site’s search rankings or indexing. It simply removes the access to the Search Console data for that specific property.
- If you are using multiple verification methods (e.g., domain, URL prefix), make sure you remove the correct version you wish to delete.
Final Thoughts:
Google Webmaster is a powerful resource for website owners looking to improve their site’s search engine visibility. By regularly using the tools and insights available, you can optimize your site’s performance, fix issues, and stay ahead in search rankings.











